Exercise 2: Importing data in R
The usual data sources can be a text file in txt or csv format or spreadsheet(excel) file in xls or xlsx. Data and R-objects can also be imported from rds, rda or rdata. Below, we will discuss these in detail. In addition you can also find some animated images showing how we can import data in RStudio for each of these file formats.
Import txt or csv
Base R-package has read.table and read.csv for importing a text or comma separated file (csv) files. Download bodydata.txt and to import it in R as,
bodydata <- read.table("_data/bodydata.txt", header = TRUE)Here the argument header is TRUE if the data has header in its first row. The argument sep takes \t, , or ; based on if the columns in the text data are tab-separated, comma-separated or separated by semi-colons. If the decimal values in the data are represented by ,, the dec argument takes the value ,. For further help see: ?read.table
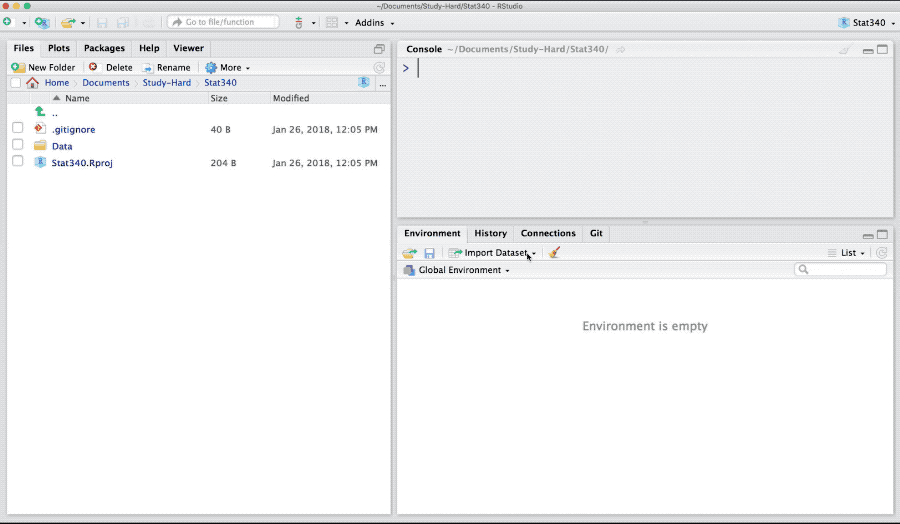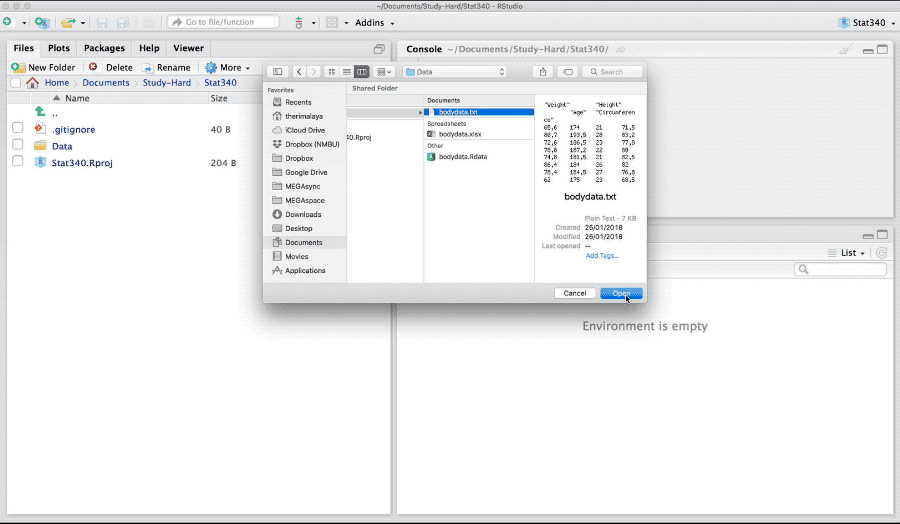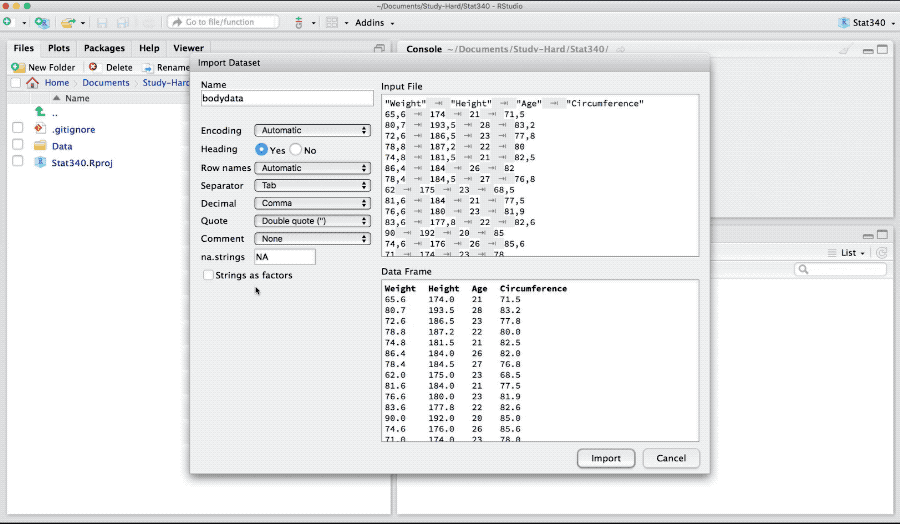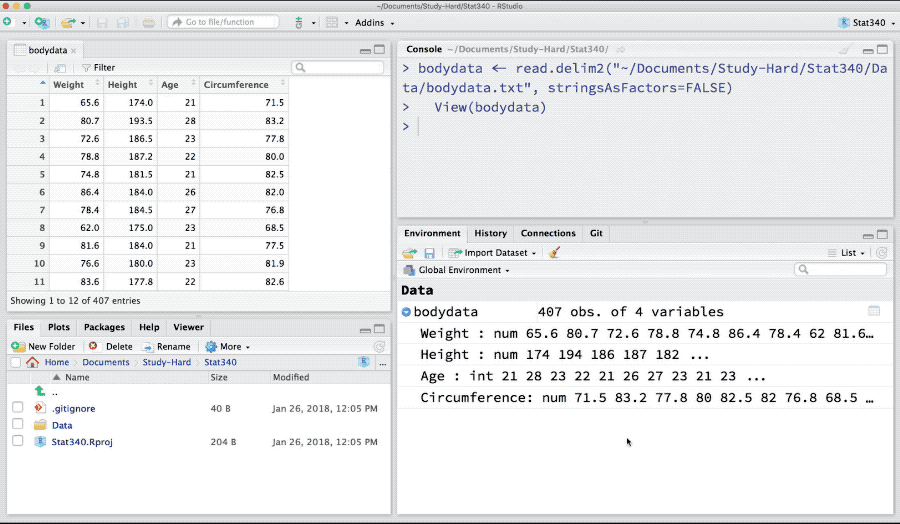
Figure 3: Import text data
Import Microsoft Excel spreadsheet
An R-package readxl helps to import excel file. If it is not installed, you should install it as,
install.packages("readxl")Download bodydata.xlsx from canvas and load it to R as,
library(readxl)
bodydata <- read_excel("_data/bodydata.xlsx", sheet = 1)For further help and arguments on this function load the library as library(readxl) and see: ?read_excel or ?read_xlsx.
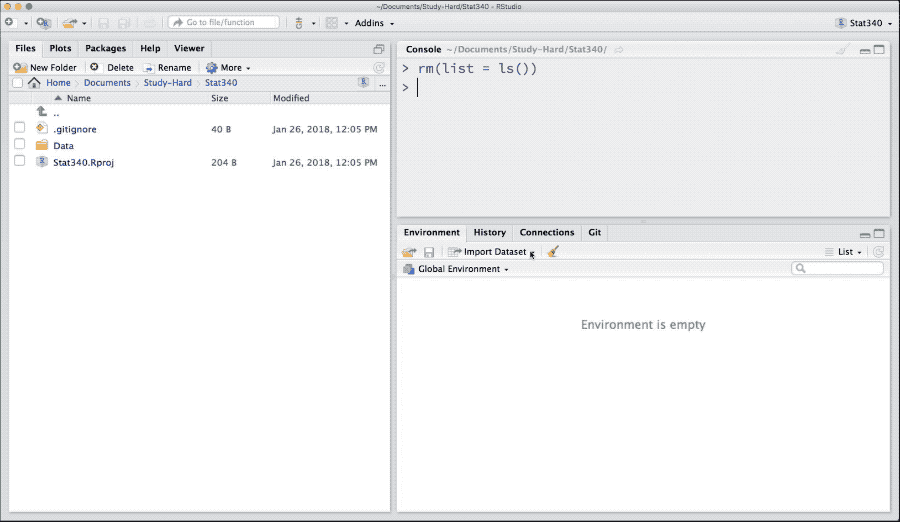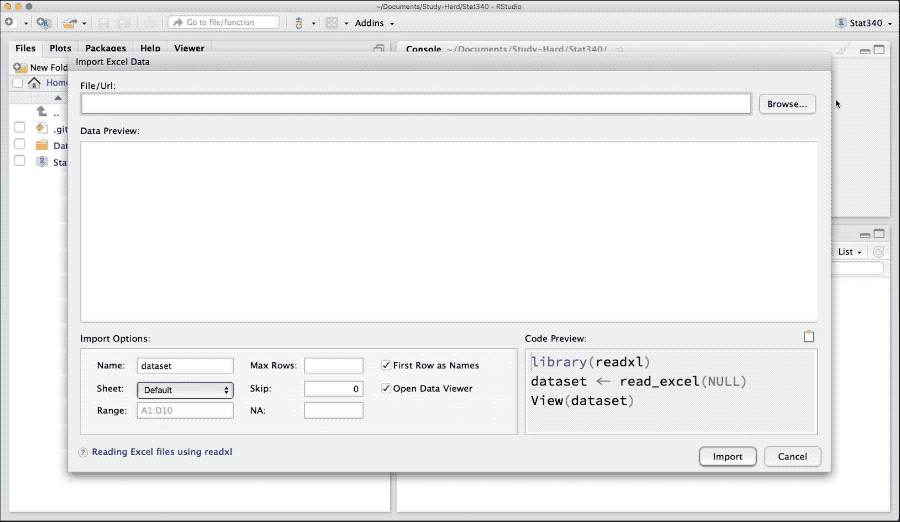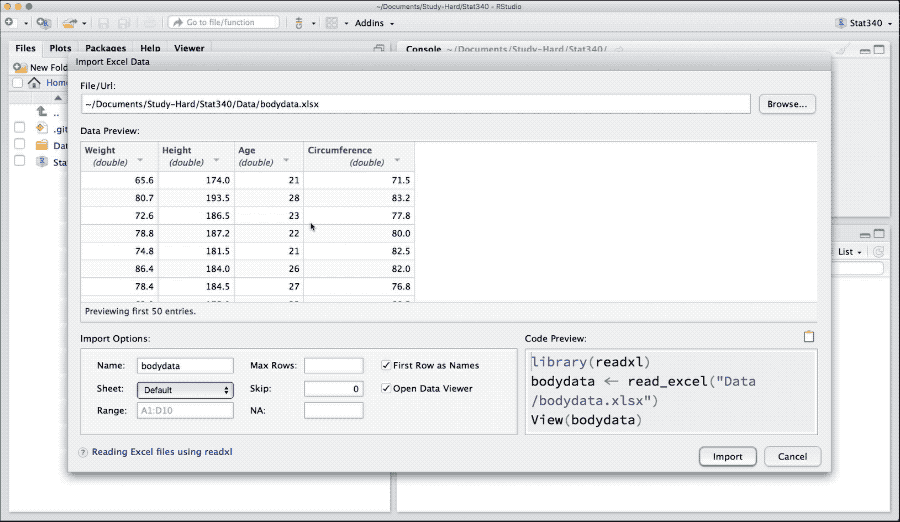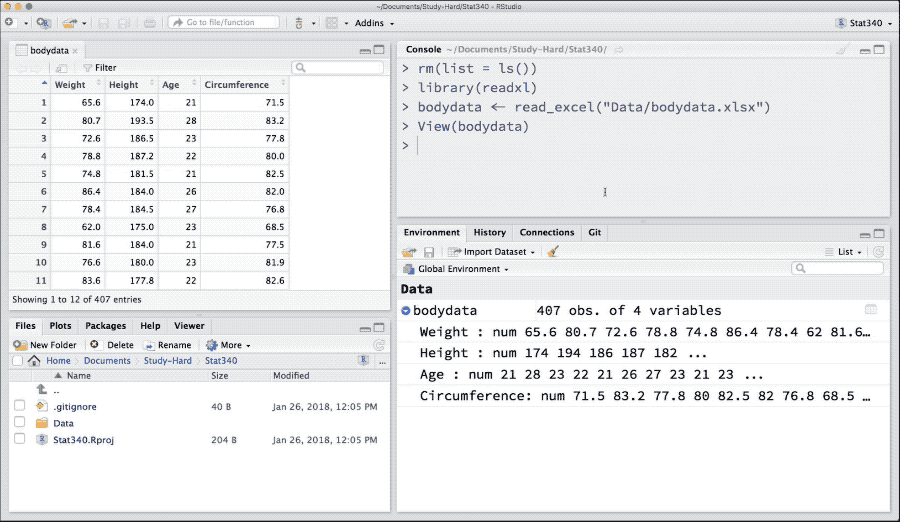
Figure 4: Import data from Microsoft Excel
Load rdata, rda or rds
One can save data, models and other R-objects in rdata or rds format. In order to load rdata, we can use load function. Download bodydata.rdata from canvas and load it to R.
load("_data/bodydata.rdata")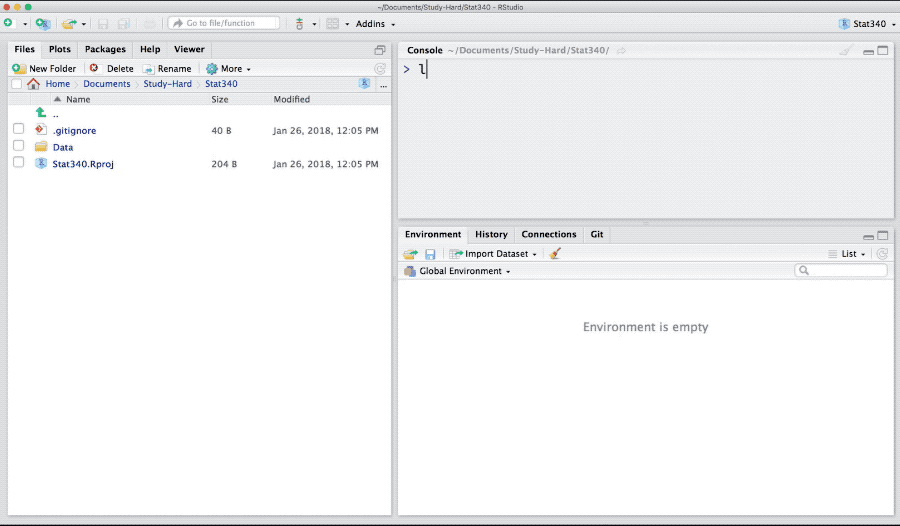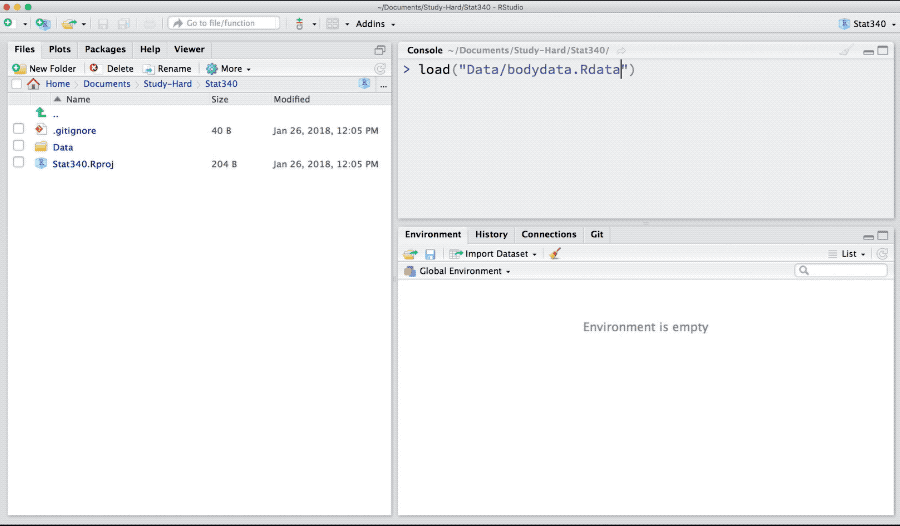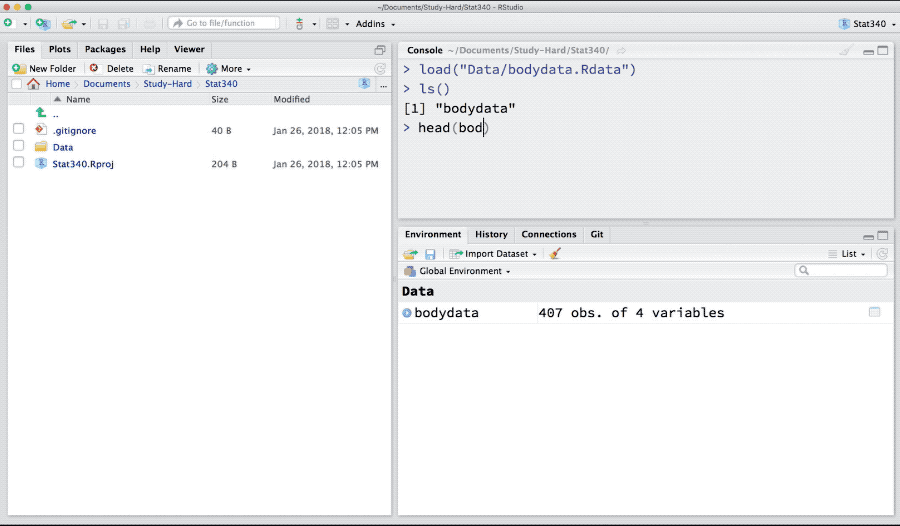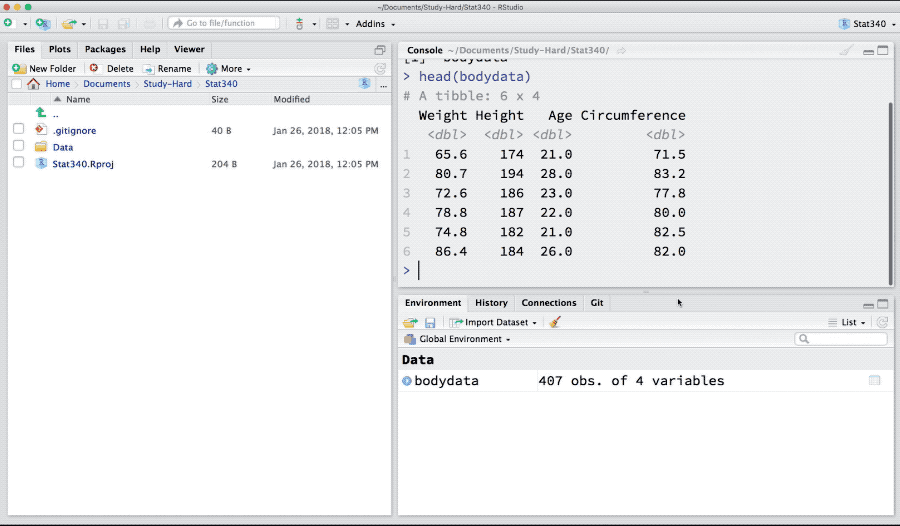
Figure 5: Import data in Rdata format
Reading data from clipboard (“pasting” copied data into an R object)
You can import data in clipboard in R. For example the data you copied in Excel or Word files.
bodydata <- read.table(file = "clipboard", header = TRUE)In Mac, you need to do,
bodydata <- read.table(file = pipe("pbpaste"), header = TRUE)This allows us to get the data from anywhere just after they are copied.
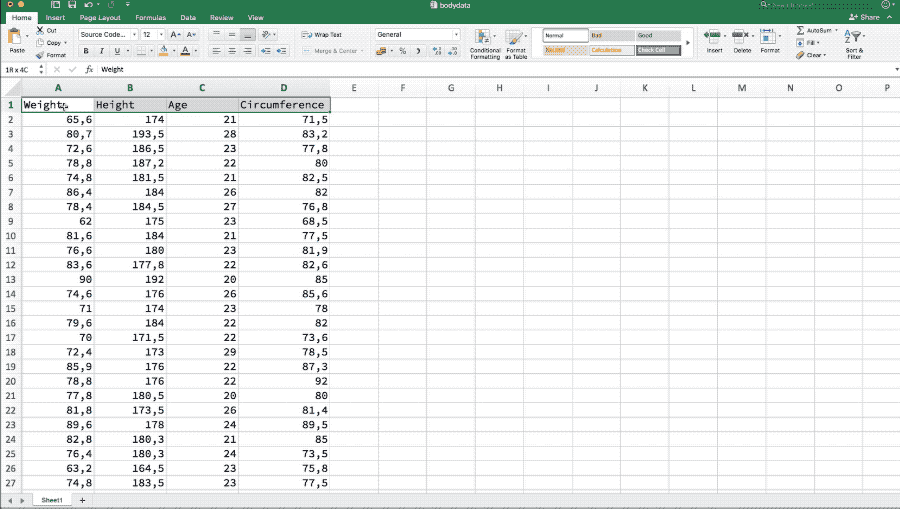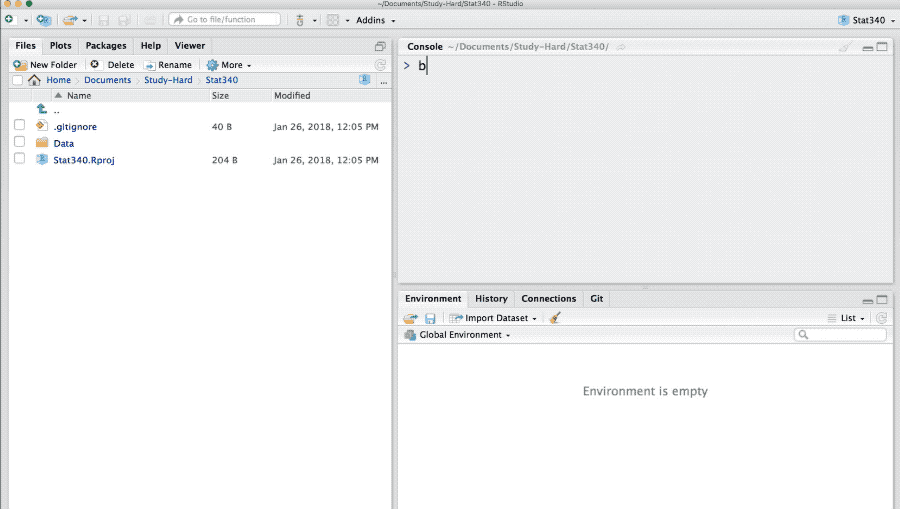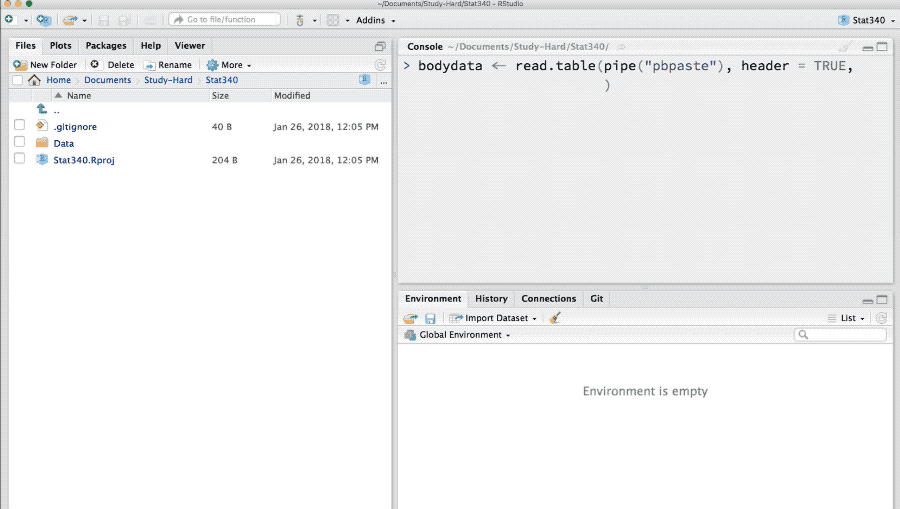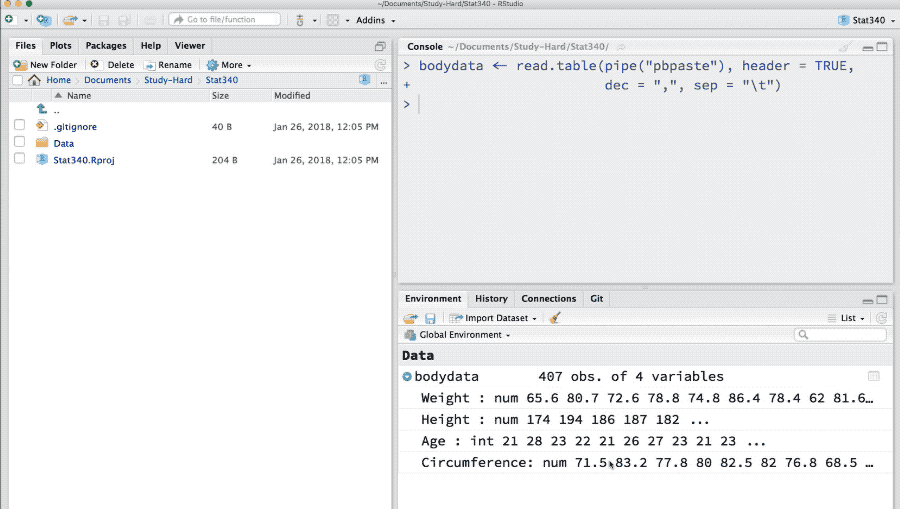
After every import in above examples, we have saved our imported data in bodydata variable. This an R-object that holds any kind of data-structures such as matrix, data.frame, list or fitted models. We can find these R-objects in “Environment” tab in RStudio.